In Jenkins, timestamps record the date and time at which various events occur, such as when a build starts when it finishes, or when a user logs in. Timestamps can help track the progress of builds, identify when problems occurred, etc.
Jenkins will typically record timestamps in ISO 8601, a standardized format for representing dates and times. They can be used in various ways, such as to generate reports or trigger other actions based on the event's time.
In Jenkins, timestamps are governed by the timestampper plugin. This plugin allows you to add timestamps to the console output of a given Jenkins job.
Jenkins Timestamper Plugin
By default, you will find the Timestamper plugin installed on your Jenkins controller. However, it is good to ensure that the plugin is installed.
Navigate to the Jenkins Dashboard -> Manage Jenkins -> Manage Plugins -> Installed Plugins.
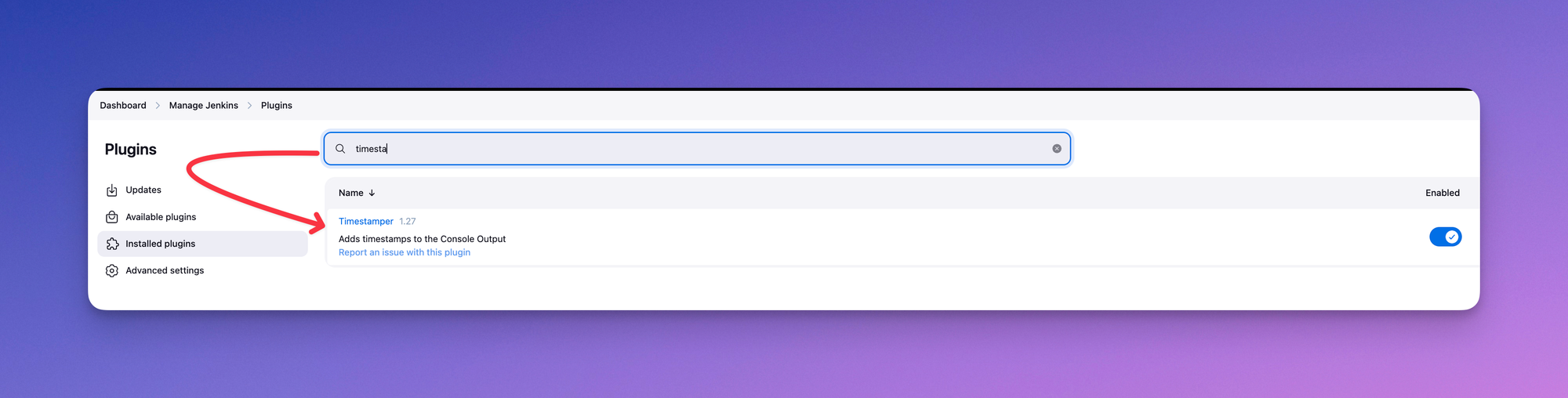
Configuring the Jenkins Timestamper Plugin
You can customize various parameters of the Timestamper plugin from the Jenkins Dashboard.
Navigate to Manage Jenkins -> Configure System -> Timestamper.
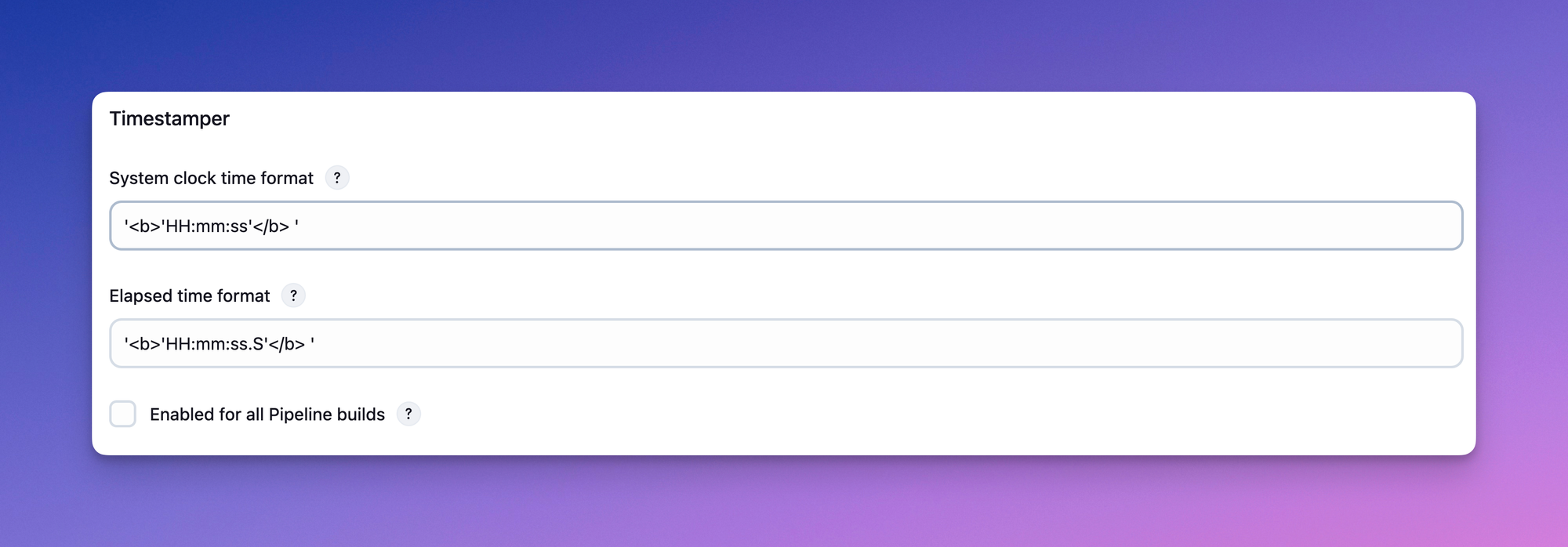
In this section, you can customize the system clock and elapsed time formats.
You can customize formats using the DurationFormats, as shown in the documentation below.
To enable the Timestamper on all Jenkins build, check the Enable for all pipeline builds checkbox and click save.
An example pipeline for timestamps is as shown:
// This shows a simple build wrapper example, using the Timestamper plugin.
node {
// Adds timestamps to the output logged by steps inside the wrapper.
timestamps {
// Just some echoes to show the timestamps.
stage "First echo"
echo "Hey, look, I'm echoing with a timestamp!"
// A sleep to make sure we actually get a real difference!
stage "Sleeping"
sleep 30
// And a final echo to show the time when we wrap up.
stage "Second echo"
echo "Wonder what time it is now?"
}
}Once enabled, a timestamp will be added to every line in the console output of a Jenkins build.
An example is shown below:
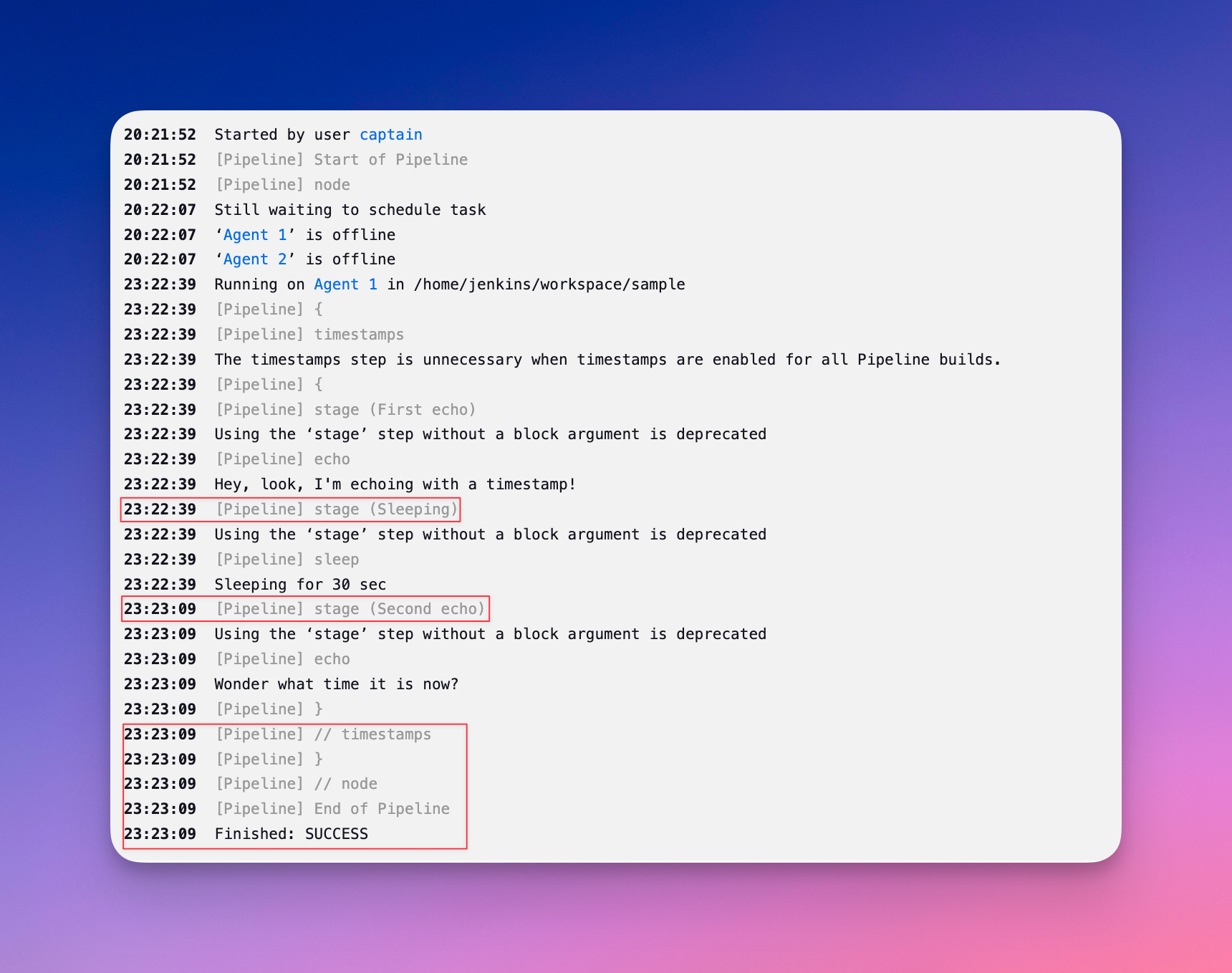
Enabling Timestamps for a Job
Sometimes, you may not want to enable the timestamps for specific jobs rather than globally.
Start by disabling the Global timestamps option as shown in the previous step.
Next, you can add timestamps in a given job by adding the timestamps option in a Jenkins pipeline.
An example is as shown:
pipeline {
agent any
options {
timestamps() // Adds timestamps to the console output
}
stages {
stage('Start') {
steps {
script {
sh 'date +%s' // Print the current timestamp in seconds
}
}
}
stage('Pausing') {
steps {
script {
sleep(time: 2, unit: 'MINUTES') // Pause for 2 minutes
}
}
}
stage('End') {
steps {
script {
sh 'date +%s' // Print the timestamp in seconds after the pause
}
}
}
}
}
By adding the timestamp() options in the Jenkinsfile, Jenkins will enable timestamps for the console output of the job.
Ending
In this tutorial, you learned how to enable, disable and customize timestamps in Jenkins pipelines.

